club foot horse cause
The chances of having a baby with Club Foot double if you or your spouse or your other children have the condition. The actual hoof will also be a size or two smaller than the other and a different shape.
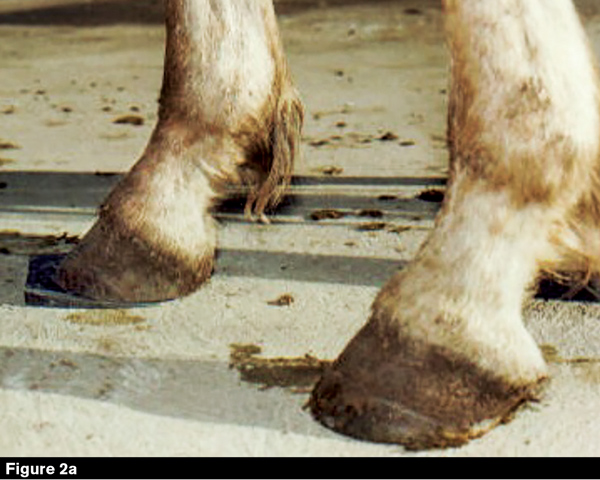
Club foot refers to a tendon flaw that causes the hoof to be very upright.

. Caused by abnormal contraction of the deep digital flexor tendon a club foot puts pressure on the coffin joint and initiates a change in a hoofs biomechanics. Club foot can occur before or after birth in foals. There is usually a reason for a horse to have mismatched feet whether it be due to conformation lameness foot disease or poor foot care Eggleston says.
Causes of Club Foot in Horses The deep flexor tendon is shorter than the bones causing a pulling on the coffin bone in the hoof which causes a deformity in the shape of the hoof Congenital deformity at birth occurring within the mares uterus likely due to multiple factors. It has even been said that horses which have a leaning posture or are in fact one-. The un-evenness in the stride and musculature will cause lameness because generally there is more stress placed on the club.
An injury to the foot is a common cause of clubfoot since it may cause a horse to shift weight to the toe to compensate for pain elsewhere. One or both feet may be affected and this condition can run in families. Club feet can also be due to a pain response.
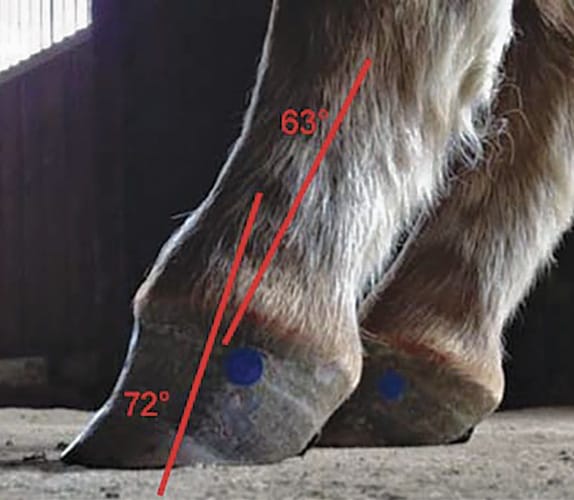
In his truck he carries five standard-sized shoes with clips and a few generic unclipped sizes. The angles when the shoes were put on were 58 degrees on the club foot and 55 degrees on the under run footThe club foot was 3 the other front was 2 78 The shoes have been on about 2 weeks. What we see externally as the equine clubbed foot is actually caused by a flexural deformity of the distal interphalangeal joint coffin joint.
Yes club feet cause lameness. Club feet are surprisingly common with up to 60 of the domestic horse population exhibiting at least minor characteristics. Club Foot also typically affects more boys than girls.
You can fix everything else and still have the back of the foot too sensitive for the horse to land on which will cause the shortened stride and resulting club foot on its own another vicious cycle. Club foot is defined as a flexural deformity of the coffin joint and is a common problem in young growing horses. Most horses only have one club.
Because horses feet differ just as much as humans in size and shape he shapes the shoes he carries to fit the foot. Recently he worked at the Smoke Rise Riding Club Horse Show in Kinnelon. After birth foals acquire club feet when the bones grow faster than the tendons.
The cause of clubfoot is unknown idiopathic but it may be a combination of genetics and environment. Causes of club foot Club foot has several possible causes. A clubbed foot it a contracted tendon meaning that the leg with the club will not be able to reach as far.
Therefore the term club foot in horses does not apply in these cases. Any club foot that has been around a while will have a sensitive unused underdeveloped frogdigital cushion. The exact cause of Club Foot is unknown.
Sometimes such an injury. What Can You Do About Uneven Hoof Growth. Often the club foot or feet are secondary to OCD lesions in the shoulder for instance says Burns.
The horse is moving better but this could just be the eggbar shoes. If its painful for the horse to put weight on that limb or favors it a little bit the flexor muscles eventually contract and pull the heel up with the horse walking more on the toe. The number one cause of a clubbed foot is genetic with OCD problems falling as the second-leading cause and a distant third cause being a bad case of ephiphysitis.
Club foot can develop in mature horses too for similar reasonsany injury or chronic pain that causes a horse to consistently favor one foot can lead to contracting and shortening of the muscles and tendons specifically the deep digital flexor tendon and muscle apparatus in that leg eventually pulling the foot into a more upright position. Several theories address the potential causes ranging from a genetic predisposition to hoof or body injury to. Unless there is a bony deformity of the foot that is causing the bone to be misshapen these cases are caused by soft tissue contraction from limited range of motion andor weight bearing in the affected limb.
Causes include nutritional issues heredity position in the uterus or injury. Not to be overlooked as a. Often club foot affects both front legs with one being more severe than the other.
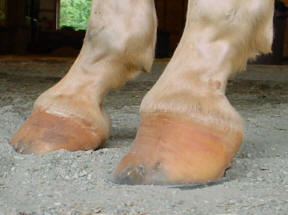
Club foot is one of the most common deformities in the horse world. The differences in growth rates that cause club feet could be the result of a number of factors including too rapid growth diet imbalances inappropriate exercise traumatic injury and inflammatory responses. Telltale signs of a club foot may include an excessively steep hoof angle a distended coronary band growth rings that are wider at the heels contracted heels and dished toes.
The condition is most often encountered in young animals and can be either congenital they are. Characteristics of a club foot are a prominent or bulging coronary band a very upright hoof wall angle a heel that doesnt touch the ground a dish in the hoof wall at the toe growth rings wider at the heel than the toe and. Example of a club foot.
They can range from uterine malposition to injuries after birth and from genetic defects to improper nutrition. Any event that leads the young horse to load its weight unequally on its front limbs puts a foal at risk for developing deformities. This condition usually is discovered in young horses when they are about four to six months of age.
Cause it bears little resemblance to the clubfoot de-formity in children referred to as congenital talipes equinovarus45 Presumably the term was coined to describe the upright or straight tubular appear-ance of the foot where there is little expansion of the hoof capsule giving a club-like appearance but. Foaling trauma foal grazing stance overly fast growth of limbs injury or even something as benign as over zealous cosmetic trimming of the toes of a foals hooves. Risk factors Boys are about twice as likely to.
The equine club foot is defined as a hoof angle greater than 60 degrees. Horses affected with club foot develop a flexural deformity of the coffin joint due to a shortening of the musculotendinous unit that starts high up in the limb and inserts on the coffin bone in the foot resulting in an upright conformation of the foot.
Defining And Fixing A Horse S Club Foot

Ballerina Syndrome Where The Heels Remain Off The Ground Even At The Download Scientific Diagram
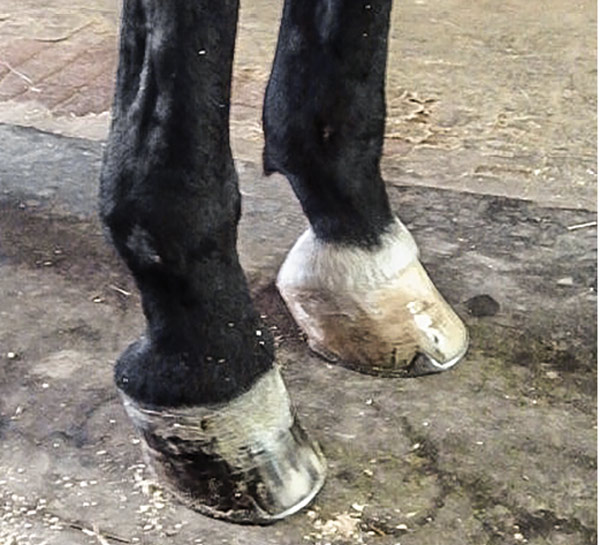
What Advice Has Been Most Helpful When You First Encounter A Club Foot
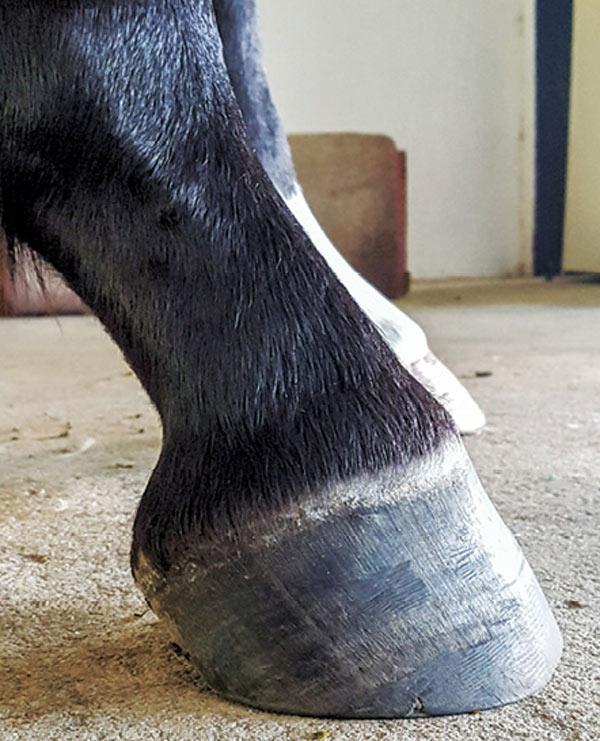
Club Foot Or Upright Foot It S All About The Angles
So Called Club Foot By James R Rooney Dmv

How D That Happen Origins And Remedies For Clubfoot Horse Racing News Paulick Report